Let’s do a Python Slice string list tuple how-to tutorial. Let’s go! 🔥🔥🔥
In Python, a slice is a feature that allows you to extract a part of a sequence type (like strings, lists, or tuples) using a range of indices. The basic syntax for slicing is [start:stop:step], where start is the index where the slice begins, stop is the index where the slice ends, and step determines the stride between each element in the slice.
If omitted, start defaults to the beginning of the sequence, stop to the end, and step to 1. Slicing is particularly useful for accessing sub-sequences within larger sequences, enabling efficient and concise manipulation of data.
Slicing Strings
Let’s give a simple example of using slicing with a string:
simple_string = "Hello, World!"
simple_slice = simple_string[7:12]
print(simple_slice)
#output
#WorldThis code creates a string simple_string with the value “Hello, World!” and then slices it using simple_string[7:12]. This slice extracts the substring from index 7 to 11, resulting in ‘World’.
For a more complex example we write the following code:
complex_string = "Python is fun!"
complex_slice = complex_string[::2]
print(complex_slice)
#output
#Pto sfnIn this more complex example string slicing example, the code takes the string complex_string with the value “Python is fun!” and applies the slice complex_string[::2]. This slice selects every second character from the entire string, resulting in ‘Pto sfn‘. This type of slicing is handy for extracting characters at regular intervals.
Let’s move on to slicing lists in Python.
Slicing Lists
Here’ is a simple example:
simple_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
simple_slice = simple_list[2:5]
print(simple_slice)
#output
#[3, 4, 5]This code demonstrates a simple use of slicing with a list. The list simple_list contains integers from 1 to 6. The slice simple_list[2:5] extracts a subset of this list, starting from the index 2 (inclusive) and ending at index 5 (exclusive). This results in a new list [3, 4, 5], which includes the 3rd, 4th, and 5th elements of the original list.
Let’s do a more complex example of slicing with lists:
complex_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
complex_slice = complex_list[1:9:2]
print(complex_slice)
#output
#[1, 3, 5, 7]In this more complex example, the list complex_list consists of integers from 0 to 9. The slicing operation complex_list[1:9:2] takes a subset of this list, starting from index 1 to index 8, but with a step of 2. This means it selects every second element in the specified range, resulting in [1, 3, 5, 7]. This type of slicing is useful for extracting elements at regular intervals from a list.
Slicing Tuples
Let’s do a simple example of slicing with tuples:
simple_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
simple_slice = simple_tuple[1:4]
print(simple_slice)
#output
#(2, 3, 4)In this simple example, we have a tuple simple_tuple containing the numbers 1 through 6. The slice simple_tuple[1:4] extracts a subset of this tuple, starting from index 1 and ending at index 3 (since the end index is exclusive in Python slicing). This results in a new tuple (2, 3, 4), which contains the second, third, and fourth elements of the original tuple.
Let’s see a more complex example:
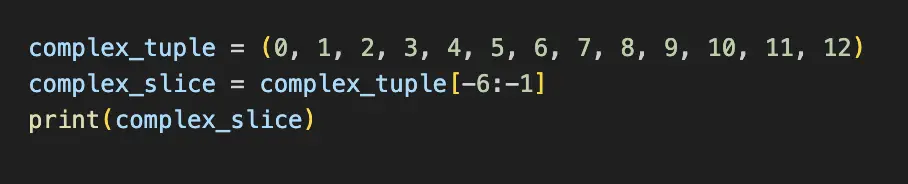
complex_tuple = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12)
complex_slice = complex_tuple[-6:-1]
print(complex_slice)
#output
#(7, 8, 9, 10, 11)In the more complex example, the tuple complex_tuple has integers from 0 to 12. The slicing operation complex_tuple[-6:-1] uses negative indices, which count from the end of the tuple. This slice starts from the sixth element from the end (which is 7) and goes up to (but not including) the last element, resulting in the tuple (7, 8, 9, 10, 11). This type of slicing is particularly useful for extracting elements from the end of a sequence without needing to know its exact length.
So there you have it, a Python Slice string list tuple tutorial with code example. Happy coding! 👌🏻👌🏻👌🏻
Checkout another great tutorial HERE.
