In this tutorial we will show you how to use python list comprehension with two or more lists.
We can use the zip function. See the below example:
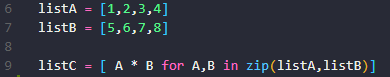
listA = [1,2,3,4]
listB = [5,6,7,8]
listC = [ A * B for A,B in zip(listA,listB)]
print(listC)
#Output
#[5, 12, 21, 32]Let’s explain what is going on here:
- We define our two lists listA and listB. Both contain numbers only.
- Our list comprehension has the job of finding the product of the nth elements of listA and listB lists.
- The zip() function in Python accepts iterables (lists, dataframes, dictionaries etc.) and returns a zip object which is itself an iterator. This iterator generates a series of tuples containing elements from each iterable supplied in the original function, in the order they were supplied. The first tuple is the first element of each iterable, the second tuple is the second element of each iterable and so on. The zip() function is evaluated left-to-right.
- Our list comprehension returns listC which is a list of the products of each element of the two lists. The product of the 1st element of each list, the product of the 2nd element and so on. A is the iterator variable for listA, B is the iterator variable for listB. Because we want the product of the nth element in each list our output expression must be A*B, which gives us the product that we are looking for.
Let’s do another example with a pandas dataframe.
import pandas as pd
data = {'Country Name': ['Sundar','Jamal','Mark','Jenny','Bob'],
'Year 1 Income':[250555,100300,45000,66000,1400000],
'Year 2 Income':[250000,110300,45000,0,2400000]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
listD = [ B - A for A,B in zip(df["Year 1 Income"],df["Year 2 Income"])]
print(listD)
#Output
#[-555, 10000, 0, -66000, 1000000]So using zip() works on dataframes also because dataframes are an iterable object. In the above example we used the list comprehension to calculate the difference in income between two years for 5 people. We simply found the difference between Year 1 Income and Year 2 Income for each person using our list comprehension.
zip() can work on more than two lists also. See below:
listE = [1,2,3,4]
listF = [5,6,7,8]
listG = [9,10,11,12]
listH = [ E+F+G for E,F,G in zip(listE,listF,listG)]
print(listH)
#Output
#[15, 18, 21, 24]
In the above we used 3 lists in our zip() function: ListE, ListF and ListG. Our list comprehension used the iterator variables E, F and G in the expression E+F+G to give us the sum of nth elements of 3 different lists. Our output is a list of 4 elements, as expected.
The above example used lists with the same number of elements in the zip() function. If they were not of the same length, the zip() function iterator would have stopped when the shortest input iterable was exhausted. Please remember this when using lists of different lengths!
Finally, we don’t have to use the zip() function. We can use nested for-loops in our list comprehension. It all depends on the problem we are trying to solve. For example, if we want to find all of the possible permutations of two different lists we can do the following:
listI = [1,2,3,4]
listJ = [5,6,7,8]
listK = [[I, J] for I in listI for J in listJ]
print(listK)
#Output
#[[1, 5], [1, 6], [1, 7], [1, 8], [2, 5], [2, 6], [2, 7], [2, 8], [3, 5], [3, 6], [3, 7], [3, 8], [4, 5], [4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 8]]So our nested for-loop in our list comprehension allowed us to generate a list of all permutations of numbers from two separate lists. We could have alternatively done this with a normal nested for-loop in the following way:
listI = [1,2,3,4]
listJ = [5,6,7,8]
listL=[]
x=[]
for I in listI:
for J in listJ:
listL.append([I,J])
print(listL)
#Output
#[[1, 5], [1, 6], [1, 7], [1, 8], [2, 5], [2, 6], [2, 7], [2, 8], [3, 5], [3, 6], [3, 7], [3, 8], [4, 5], [4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 8]]
The above nested loops work the same but list comprehensions, as we have seen, require less code and are more readable.
Find the full source code HERE and other great tutorial on list comprehensions HERE. Thanks for reading. 👌👌👌
